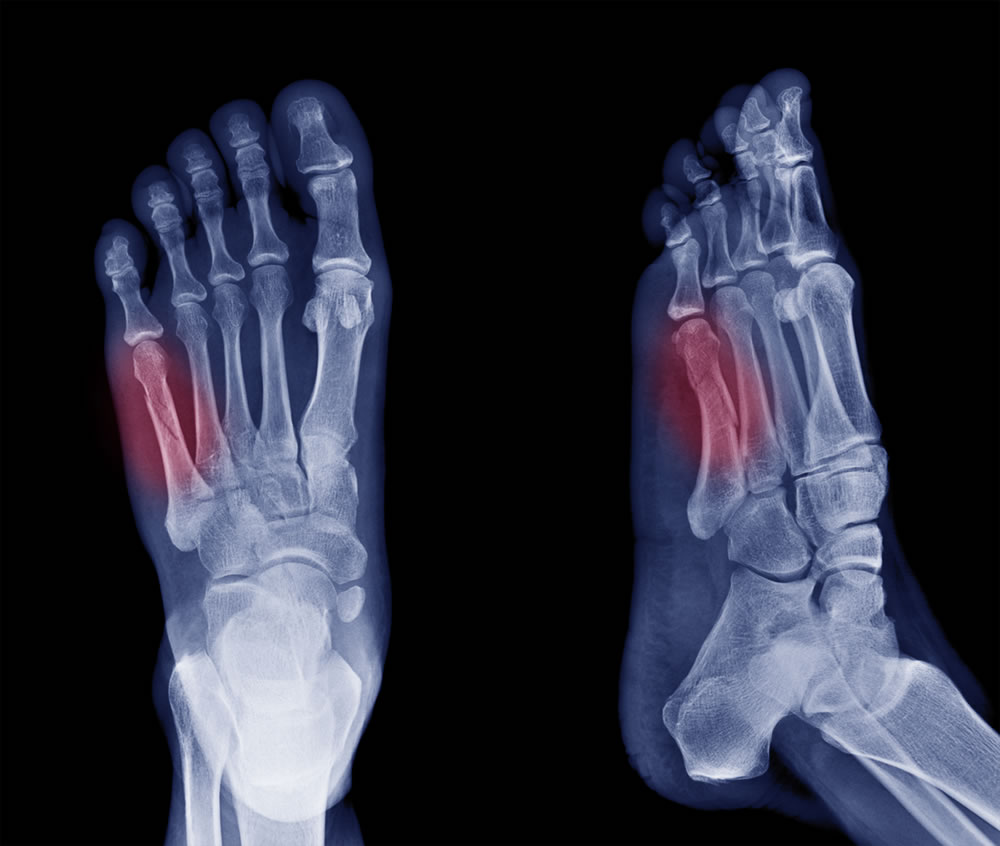
Foot Fracture
A foot fracture refers to a break or crack in one or more of the bones of the foot. Fractures can occur in various parts of the foot, including the toes, metatarsals (long bones in the middle of the foot), and the tarsals (bones in the hindfoot).
Causes
- Trauma: Direct trauma or impact to the foot, such as a fall, sports injury, or automobile accident, can cause fractures.
- Overuse or Repetitive Stress: Chronic stress on the foot, often from activities like running or jumping, can lead to stress fractures.
- Osteoporosis: Weakened bones due to conditions like osteoporosis can increase the risk of fractures.
- Accidents: Workplace accidents, falls from heights, or other accidents can result in foot fractures.
Symptoms
- Pain: Intense pain at the site of the fracture.
- Swelling: Swelling and bruising may occur around the injured area.
- Deformity: In severe fractures, there may be a visible deformity or misalignment of the affected part.
- Inability to Bear Weight: Difficulty or inability to put weight on the injured foot.
- Tenderness: The affected area is tender to touch.
Treatment
- Immobilization: Most foot fractures require immobilization through the use of a cast, splint, or walking boot to allow proper healing.
- Rest and Elevation: Elevating the foot and avoiding weight-bearing activities help reduce swelling and promote healing.
- Ice Therapy: Applying ice to the injured area can help control pain and swelling.
- Pain Medications: Over-the-counter or prescription pain medications may be recommended for pain management.
- Physical Therapy: Rehabilitation exercises may be prescribed to restore strength and flexibility after the initial healing phase.
Complications
- Delayed Healing: Factors such as poor blood supply, inadequate immobilization, or certain medical conditions can contribute to delayed healing.
- Nonunion or Malunion: In some cases, fractures may not heal properly, leading to nonunion (failure to heal) or malunion (healing in a misaligned position).
- Chronic Pain: Some individuals may experience chronic pain or stiffness in the affected area.
- Post-Traumatic Arthritis: Fractures can increase the risk of developing arthritis in the affected joint.
Prompt and proper medical evaluation is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. If you suspect a foot fracture, seek medical attention to prevent potential complications and ensure optimal healing.
Foot Fracture Surgery
Surgery for foot fractures is considered when the fracture is severe, displaced, or when conservative treatments fail to achieve proper healing. The specific surgical approach depends on the type and location of the fracture. Here are some common foot fracture surgeries:
Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF)
- Procedure: In this surgery, the surgeon makes an incision to access the fractured bones, aligns them into the correct position, and then uses screws, plates, or other hardware to stabilize and hold the bones together.
- Indications: ORIF is commonly used for fractures that are displaced, unstable, or involve joints.
Closed Reduction with Percutaneous Pinning
- Procedure: The surgeon aligns the fractured bones without making a large incision. Small wires or pins are then inserted through the skin and into the bones to maintain alignment.
- Indications: Percutaneous pinning is often used for certain types of fractures, particularly those involving the toes.
External Fixation
- Procedure: This involves placing metal pins or screws into the bones above and below the fracture, which are then connected externally by a metal frame. This stabilizes the fracture from the outside.
- Indications: External fixation is used for severe fractures, open fractures, or cases where traditional internal fixation may not be suitable.
Intramedullary Nailing
- Procedure: A metal rod (nail) is inserted into the medullary canal of the long bones, such as the tibia or metatarsals, to provide stability and support for the fractured bone.
- Indications: Intramedullary nailing is often used for long bone fractures, especially those with significant displacement.
Joint Fusion (Arthrodesis)
- Procedure: Fusion of a joint involves removing damaged cartilage and stabilizing the bones to promote fusion. This is often done for fractures involving joints or for certain types of severe arthritis resulting from a previous fracture.
- Indications: Arthrodesis is considered when maintaining normal joint movement is not critical, and stability is a higher priority.
Soft Tissue Repair
- Procedure: In some cases, surgery may be required to repair damaged soft tissues, such as tendons or ligaments that are associated with the fracture.
- Indications: Soft tissue repair is necessary when there is significant damage to the surrounding structures that affects the stability and function of the foot.
It's important to note that not all foot fractures require surgery, and the decision is based on the specific characteristics of the fracture and the individual's overall health. The choice of surgical intervention and the type of hardware used are determined by the orthopedic surgeon after a thorough assessment of the fracture. Post-surgery, rehabilitation and physical therapy are often essential to restore function and mobility.
To know more kindly contact the best orthopaedic surgeon Dr. Rahul Modi for further queries.
This surgery is frequently performed by the best orthopaedic surgeon Dr. Rahul Modi for treating Foot Fracture.